
From October 29th to 31st the FIWARE Foundation will be returning to Barcelona (Spain) for the IoT Solutions World Congress, the largest IoT event in the world. This year, we are going big! The FIWARE Foundation is part of one of the ten selected testbeds to be presented at the event.
In collaboration with International Data Spaces Association (IDSA), PROSTEP AG, prostep IVIP, Innovalia, and several other key Industrial partners, the FIWARE Foundation has contributed to the creation of a testbed that demonstrates how data sovereignty, blockchain, and open source technologies can be jointly used to break information silos providing at the same time a seamless and controlled exchange of data across digital twins.
The testbed originates from Boost 4.0, MIDIH lighthouse projects of the EU, and the SAMPL project (funded by the German Ministry of Energy and Economics) as well as from industry demand for access to a representative neutral experimentation environment. Here, digital twin benefits could be assessed. Moreover, the feasibility of the cost-effective implementation of digital threads based on open international standards, data sovereignty, and digital platform interoperability could be demonstrated on a meaningful complex product, involving comprehensive (big) data-driven advanced engineering/production IoT processes.
There is a special bond between the digital twin and the physical world it represents. The digital twin has largely been a PLM concept for design and performance simulation of discrete products. Now, new kinds of digital twins are available to support and improve specific manufacturing plant production processes through Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) and obtain a better understanding of the product performance in operation through IoT.
Each of these various kinds of digital twins has been developed as a siloed solution, each dealing with different manufacturing processes across the product lifecycle. The data exchange among digital twins breaking these silos opens the door for manufacturers to receive unprecedented insights, visibility and automation opportunities. This, in turn, leads to efficiency improvements in product design, product performance and manufacturing process operations.
The testbed demonstrates how IDSA and FIWARE open source technology, as well as SAMPL secure 3D printing technology, can be used to provide a seamless and controlled exchange of data across digital twins based on open international standards (prostep ivip, QIF) and the SAMPL blockchain technology. This will allow companies to dramatically improve cost, quality, timeliness, and business results through enhanced traceability, process workflow automation, and improved product and manufacturing process knowledge.
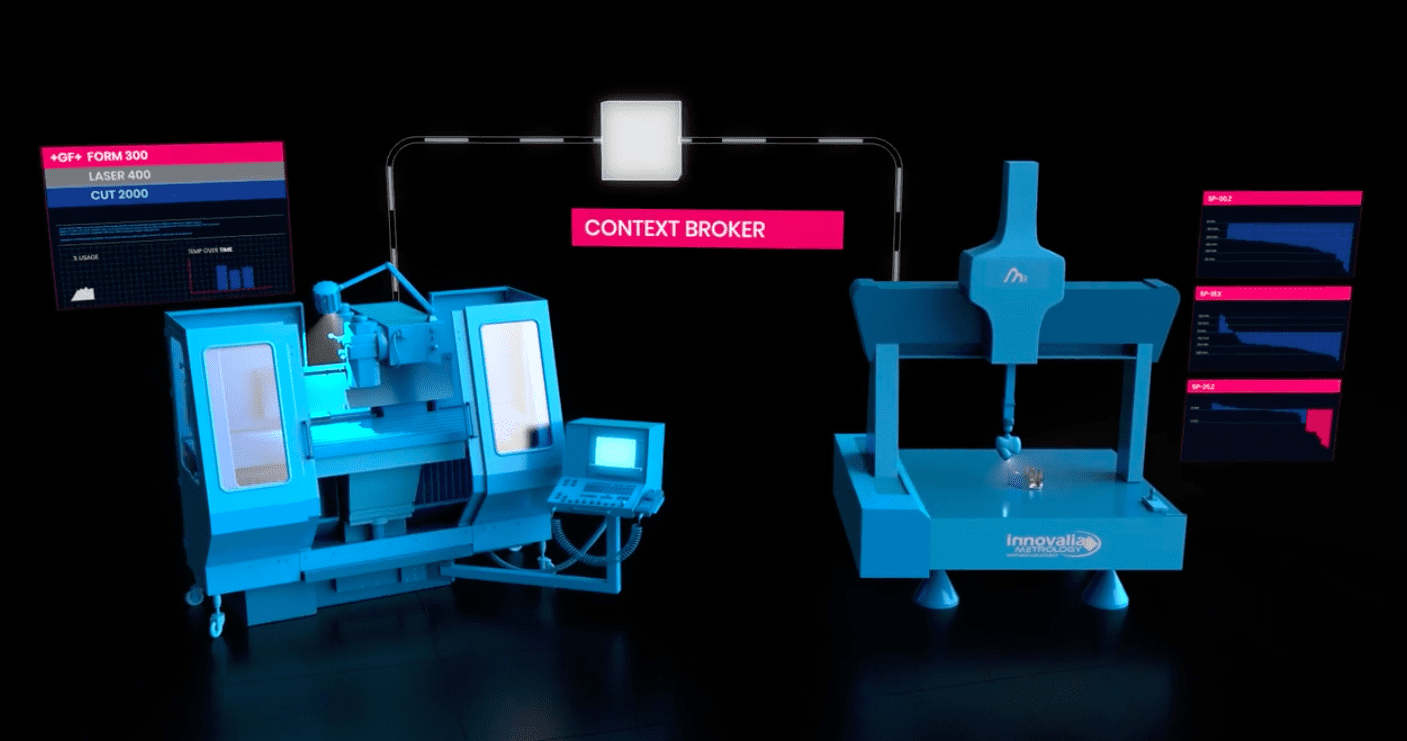
Data Exchange Between Machines in the Shopfloor for Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM)
Currently, machines chained on the shop floor as part of the manufacturing process are working as information silos. They are ‘physically’ connected because the part treated by one machine is passed to the next machine in the chain, which in turns treats this part and passes it on to the next. Each of those machines generates a large amount of data, which so far has been used to monitor and improve the processes and tasks each machine performs. However, systems associated with each machine are not designed to exploit data from others when improvements can be gained if the data from one machine ‘feeds’ the systems connected to the other and if such exchange is made in a way that is secure. Access control terms and conditions established by each individual machine provider are hereby preserved and the shop floor operator is also the final decision-maker. The operator, therefore, defines what is exchanged and what for, and whether it goes out of the factory.
The testbed demonstrates how factories can benefit from IDS concepts and FIWARE open source technology. It showcases the enhanced functionalities for the improvement of processes or the support of smart decisions, through the management of context data exported by the factory.



